





Douglas Adams

|






|
Editor: Douglas Adams |
|
|
|
The Future Tenses [Table Format]
Notice that like the past and present, the only part of the basic formula for the continuous and perfect forms that changed from the basic pattern is the "be" and "have" Like the past and present tenses, learning the formulas for the future tense verbs is only the beginning and students must learn how to use these tenses, so let's look at a final example. Ten years from now Tom will be an engineer, and he will be working for Boeing. He will have graduated from college and will have been continuing to study math
In this short example, we can see each of the four future tenses in context, can ask students to identify them, and when each of these actions will happen, placing them on a time line to see their relationship to one another. As with the other tenses, we can use the simple future and future continuous tenses to describe some actions that will happen or will be happening at some point in the future. In other words, these tenses place us at some particular point of reference in the future, and show us what will be happening at that point in time.
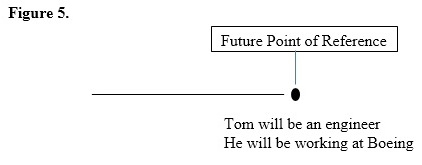
An examination of our sample paragraph also reveals that the future perfect and future perfect continuous tenses are used to talk about things that will happen or will be happening before the simple future and future continuous actions. In fact, just as in the past and present, we can think of the future perfect tenses as the before tenses since they are always used for actions that happen before some future point of reference even if that point is merely implied and not directly stated.
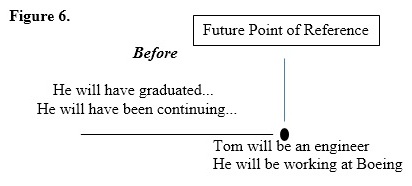 *Although all the actions in our little example will happen after now, the future perfect tenses are still the before tenses since they will happen before a future point in time. In conclusion, this pattern of the simple and continuous tenses establishing a point of reference in time and the perfect and perfect continuous tenses describing actions happening before that point is repeated for all the tenses (past, present, and future). Of course, teachers still need to show their students the negative and question forms for these tenses, but the basic pattern of usage remains the same, and helps students see the English tenses for what they are, an organized system with predictable patterns that can be inferred and more easily understood and applied.
Go on to
A day-by-day set of lesson plans
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
http://www.tesltimes.org |